
Instance Mail from KisoLabs protects your privacy and reduces spam by providing you with disposable email addresses that forward to an email account of your choice.
This is useful in many different circumstances:
With Instance Mail you can give a different email address out to each website that requires one, and shut off any address when you no longer need it. That will effectively stop spam from that site (and any mailing lists to which they might add you).
Instance Mail addresses don't expire, and there is no limit on the volume of mail you can receive. Each address is unique and cannot be changed, but you do have a choice of domain names for any address.
Unlike most other anonymous/temporary email providers, KisoLabs lets you keep track of your addresses in one place and gives you the ability to turn on spam and virus filtering. We also give you full reporting and access to raw log files to help you track down spammers!
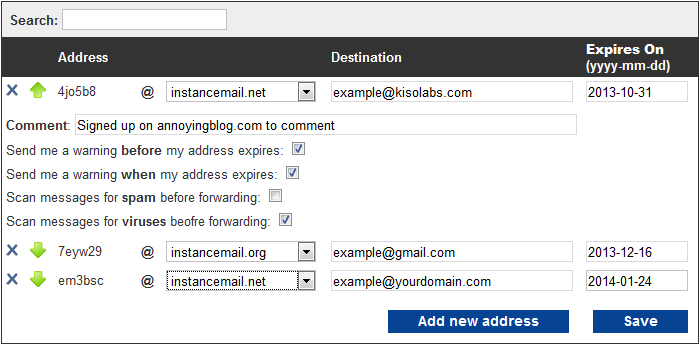
When you first view your Instance Mail service, nothing will be listed under "Email Addresses and Destinations". To add your first address, click the "Add new address" button. A new address will be assigned to you, at which point you can select a different domain, whether you want spam and virus filtering, and the destination for emails that are sent to your address.

Setting up an Instance mail address is easy. All you need to do is tell it where you want your emails to go, and then copy down the Instance Mail address. Each field and option is described below:
When you no longer want to receive email to an address, click the  button to remove it. The row will be greyed out, but the address will not be removed
until you press the "Save" button. If you change your mind, click the
button to remove it. The row will be greyed out, but the address will not be removed
until you press the "Save" button. If you change your mind, click the  button to undo the removal.
button to undo the removal.
Once an address is removed from the list of addresses and destinations, anyone sending email to that address will receive an error and mail will not be forwarded to your destination email account.
If you remove an address by accident, don't panic! Just check out the section on "Expired and Disabled Addresses"! You can restore any address that you remove.
The address is composed of two parts: The username (before the @) and the domain (after the @). So for the sample address 4jo5b8@instancemail.net, 4jo5b8 is the username and instancemail.net is the domain.
The destination is your real email address. That's where the messages will be forwarded to when they're sent to your Instance Mail address. No one sending mail to your Instance Mail address will ever see your real email address (unless you reply back to them from your real email account, of course).
The date on which this address will stop working. By default the expiration date is 120 days in the future. You can change the date so that the address will stop working earlier, which can be useful in preventing a deluge of spam.
Once your address is set up, you can go back into your Instance Mail configuration at any time and change the date. You're allowed to extend the expiration to any day up to 120 days from today. For example, if you created an address on 2013-09-01 and returned to KisoLabs 30 days later on 2013-10-01, you could set the expiration date to 2014-01-29 (which is 120 days from 2013-10-01). You can keep your Instance Mail address active forever if you keep moving the expiration date forward. (But why would you want to?)
For more options, click the  button next to an address. Those options are discussed below:
button next to an address. Those options are discussed below:
Adding a comment can be quite useful in determining why you created that Instance Mail address, and if you need it any more.
By default you will receive a warning 3 days before your address expires, and another warning when it does expire. The warning emails will be sent to whichever address you specify in the "destination" field. You can uncheck those options to disable the emails.
Select anti-spam to have all messages that are sent to your Instance Mail address scanned by our spam filters before they're forwarded to your destination email address. Our filters are more sure about some spam messages than others, so in some cases a spam message may find its way through.
Select anti-virus to have all messages that are sent to your Instance Mail address scanned by our virus filters before they're forwarded to your destination email address. You will receive a notification email whenever our filters find a virus, but you will not receive the original message which contained the virus. (Remember, no anti-virus is ever perfect, so if you're not sure if an attachment is safe or not, don't open it!)
When you set an expiration date for one of your email addresses, it will be disabled at the end of that date. So, if you set the expiration date as 2013-08-31 your address will stop working at approximately 12 AM on 2013-09-01. Please note that there may be some delay in disabling the address, so you may receive emails during the early hours of 2013-09-01.
We'll send an email to you 3 days before an Instance Mail address is going to expire. You'll receive another email when it has expired.
We've heard this question from a few people: I set my expiration date to a day in the past, but it's still showing up as an active address in my Instance Mail configuration and I can still receive emails that are sent to it. Why isn't it disabled?
If you set an address to expire in the past, it will not actually be removed from our system until we process the expirations of all Instance Mail addresses. This happens several times per
day, but your address may indeed continue working for a while. If you want your address to stop working immediately, click the  button and then
click "Save".
button and then
click "Save".
Even though you cannot change the username of your Instance Mail address (that's the part before the @ sign), you can change the domain (the part after the @ sign) at any time. When you change the domain, you will no longer be able to receive email at the original domain.
For example, if you were assigned the address 27jdw9th and chose the domain instancemail.net then any email sent to 27jdw9th@instancemail.net would be forwarded to you. If you later changed the domain to anonemail.us then any email sent to 27jdw9th@anonemail.us would be forwarded to you, but email sent to 27jdw9th@instancemail.net would be bounced back to the sender.
At this time we do not offer custom usernames or custom domain names with our Instance Mail service. However, if you are assigned a username that you don't like then you can always create another address -- they're unlimited!
If you do need disposable "vanity" email addresses, consider purchasing our Forwarder service. It allows you to use your own domain name and create as many forwarding addresses as you'd like.
Short answer: NO.
You're probably here because you want to avoid spammers and spam. At KisoLabs we pride ourselves on being part of the solution and not part of the problem. The only emails you will receive from KisoLabs to an address that you specify in the destination field are address expiration warnings (but only if you choose to receive them). We will not send you advertisements or solicitations to buy stuff from us, and we will never share your email address with anyone else unless you specifically say it's OK.
Of course if you use the same email address for your KisoLabs account as in the destination field you'll continue to receive any important emails from KisoLabs about your other services (if you have any), as well as login notifications and multi-factor authentication messages (if you choose to receive them), billing notifications (if you have any paid services), and usage quota notifications (if any are applicable to your services). But we still will not send you advertisements or solicitations to buy stuff from us, and we will never share your email address with anyone else unless you specifically say it's OK.
Full text logs for your services are available here.
Mail logs are formatted as space-delimited files with quotes enclosing any field that contains a space as content. The general format of the log is as follows:
Each of the fields is described below:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Date Queued | date | The UTC date and time that the message was queued. The format is: yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss yyyy is the 4-digit year. MM is the month (01-12) with leading zeroes. dd is the day of the month with leading zeroes. HH is the hour (00-23) with leading zeroes. mm is minutes ss is seconds |
| Date Last Processed | date | The UTC date and time that the message was last processed. If delivery could not be made
this date/time will be updated at every following delivery attempt. The format is: yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss yyyy is the 4-digit year. MM is the month (01-12) with leading zeroes. dd is the day of the month with leading zeroes. HH is the hour (00-23) with leading zeroes. mm is minutes ss is seconds |
| Queue Id | hexadecimal (string) | The queue id assigned by the KisoLabs mail server. This value does not have any real meaning for the purposes of log analysis, but can be useful when working with KisoLabs' support team to resolve email delivery issues. |
| Message Size | integer | The size of the message in bytes. |
| Client IP | IP address (string) | The IP address of the SMTP client that relayed the message to the KisoLabs mail server. |
| Client Host | string | The host name of the SMTP client that relayed the message to the KisoLabs mail server. This is the host name reported by the client with the HELO (or EHLO) command, and does not necessarily represent the DNS entry that resolves to the Client IP field. |
| Message Id | string | The message identifier (this is usually generated by the first SMTP server to relay the message). The
message identifier should be globally unique, and therefore may assist you in debugging mail delivery issues. The KisoLabs mail servers will not alter the message identifier, but in rare cases it may be modified in transit by an upstream or downstream server. |
| From Address | string | The email address of the sender of the message. |
| To Address | string | The email address to which the message will be delivered. For services that forward messages, such as Forwarder and Instance Mail, this field contains the ultimate destination address (in other words, the address to which the message was forwarded). |
| Original To Address | string | The email address to which the message was sent, if different than the To Address field. For services that forward messages, such as Forwarder and Instance Mail, this field contains the alias address defined in your service's configuration. For all other types of service, this field will contain a single dash (-) to indicate that it is unused. |
| Status Text | string | The textual description of the status code representing the delivery status of the message. This field may not be populated until
the message is delivered to, rejected by, or a timeout is reached for the destination mail exchanger. If the field is unpopulated it will be represented by a single dash (-). |
| Status Code | integer | The status code representing the delivery status of the message. This field may not be populated until
the message is delivered to, rejected by, or a timeout is reached for the destination mail exchanger. If the field is unpopulated it will be represented by a zero (0). |
| Spam (Virus) Status | string | The status reported by the spam and virus filter. If spam and virus filtering are disabled on your service, or if
spam and virus filtering were not completed for a message, this field will not be populated. If the field is unpopulated it will be represented by a single dash (-). |
| Spam Hits | decimal | A number representing the strength of the assertion by the spam filter that the message is spam. The number is qualitative, so the general rule is that a higher number will indicate that the message is more likely to be spam. |
| Last Delivery IP | IP address (string) | The IP address of the host to which the message was last delivered. This will be the address of the next-hop SMTP server
when delivery is successful. Important: If the address shown is 127.0.0.1 that indicates that it was not delivered externally, and was re-queued by the KisoLabs SMTP server. This is not an error condition, and will always occur when a message is blocked as spam, or blocked because it contains a virus. It may also occur when a message could not be delivered and is awaiting redelivery, however in that case this field may also contain a dash (-). |
It is important to remember that the mail logs represent the transactional nature of the SMTP message workflow.
In other words, when a message is received by the KisoLabs MX servers, the receipt of that message is logged. The message is then (if your service is so configured) scanned by our spam and/or virus filters, which is also logged. When delivery is attempted, that attempt is logged (and may be logged multiple times). When delivery succeeds, that is logged as well.
The logs for your MX service are generated by aggregating all of those log messages into one line. As such, a log line (or log file) may be updated retroactively when a new event occurs. For example, the following may take place:
In that example, a log line will be written into your service's log file for 2012-03-15 showing that the email was received by KisoLabs' server, but will not show delivery having been made. Approximately 24 hours later, your services log file for 2012-03-16 will be generated, but that log file will contain no information about the email in the example. Instead, the log file for 2012-03-15 will have been retroactively updated to include the final delivery status.
For most KisoLabs MX services, email messages can be queued for up to 30 days. Therefore it is possible that a log file that is 30 days old may be updated with the status of a message.
In some cases, an ill-formatted email message will not be locatable across transactional steps. This is particularly common when the message is spam and does not contain a message id (or the message id is not unique, or is too short to be globally unique). In that case, the message may cause more than one line to appear in your service's logs.
For the sake of example, five log lines are shown below for the imaginary recipient domain example.com.
The meanings of each of the sample lines are discussed below:
A message was receieved by the KisoLabs mail exchanger and queued on March 15, 2012 at 10:56:28 PM UTC from bob@sample.com to matt@example.com. The message size was 1,292 bytes, and was relayed from 10.203.80.101 (having the host name of mx01.sample.com). It was relayed to 172.16.54.92 with status code 250 ("sent") on March 15, 2012 at 10:56:30 PM UTC. It passed spam filtering, and was not considered to be spam ("Passed" 0.2781).
A message was receieved by the KisoLabs mail exchanger and queued on March 15, 2012 at 10:58:14 PM UTC from fred@flintstones.org to barney@example.com. The message size was 2,173 bytes, and was relayed from 192.168.78.22 (with an unknown host name). It was relayed to 10.88.22.11 with status code 250 ("sent") on March 15, 2012 at 10:58:15 PM UTC. It passed spam filtering, but was considered to have some characteristics of a spam message ("Passed SPAMMY" 10.2032).
A message was receieved by the KisoLabs mail exchanger and queued on March 15, 2012 at 11:01:45 PM UTC from homer@evergreent.com to sales@example.com. The message size was 2,159 bytes, and was relayed from 172.16.250.33 (having the host name of mail.simpsons.net). It was relayed to 10.3.1.87 with status code 250 ("sent") on March 20, 2012 at 9:32:18 AM UTC. It passed spam filtering, but was considered to have some characteristics of a spam message ("Passed SPAMMY" 18.3999).
This line shows a case where a message could not be delivered to the next mail exchanger for almost 5 days (the difference between the Last Processed and Queued dates). This would usually represent an issue with your mail server where it was inaccessible when the KisoLabs mail exchanger attempted delivery.
A message was receieved by the KisoLabs mail exchanger and queued on March 15, 2012 at 11:02:25 PM UTC from wentworth@uwnto.de to gesundheit@example.com. The message size was 2,181 bytes, and was relayed from 10.58.244.148 (with an unknown host name). The next mail exchanger (e.g. your mail server) responded on March 15, 2012 at 11:02:25 PM UTC with the status code 550 ("rejected"), most likely because the recipient ("gesundheit@example.com") did not exist. It passed spam filtering, and was not considered to be spam ("Passed" 1.4420). Note that the last delivery IP address is shown as 127.0.0.1 because the message was not relayed.
A message was receieved by the KisoLabs mail exchanger and queued on March 15, 2012 at 11:03:01 PM UTC from lannister@westeros.net to tyrion@example.com. The message size was 5,129 bytes, and was relayed from 10.105.99.152 (having the host name of www.somesite.org). The message has just entered the system, and so there is no delivery status nor spam status.